
Understanding Hypervisors: Types, Usefulness, and Benefits
In the realm of modern computing, virtualization has become an indispensable tool for businesses and developers alike. At the heart of this technology lies the hypervisor, a critical component that enables multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a single physical machine. Hypervisors have revolutionized the way we approach computing, offering a myriad of benefits, from improved resource utilization to enhanced system security.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of hypervisors, exploring their various types, the usefulness they bring to different environments, and the benefits they offer to organizations of all sizes.
What is a Hypervisor?
A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor (VMM), is a piece of software, firmware, or hardware that creates and manages virtual machines (VMs). By abstracting the hardware from the operating systems, hypervisors allow multiple operating systems to share a single physical host, each running in its own isolated environment. This capability is the foundation of virtualization, which is essential for cloud computing, server consolidation, and more.
Types of Hypervisors
Hypervisors are generally classified into two main types: Type 1 (Bare-Metal) and Type 2 (Hosted). Each type serves different purposes and is suitable for various use cases.
Type 1 Hypervisors (Bare-Metal)
Type 1 hypervisors, often referred to as bare-metal hypervisors, run directly on the host’s hardware, without the need for a traditional operating system. They are highly efficient and provide superior performance, making them ideal for enterprise environments where high performance, scalability, and stability are critical.
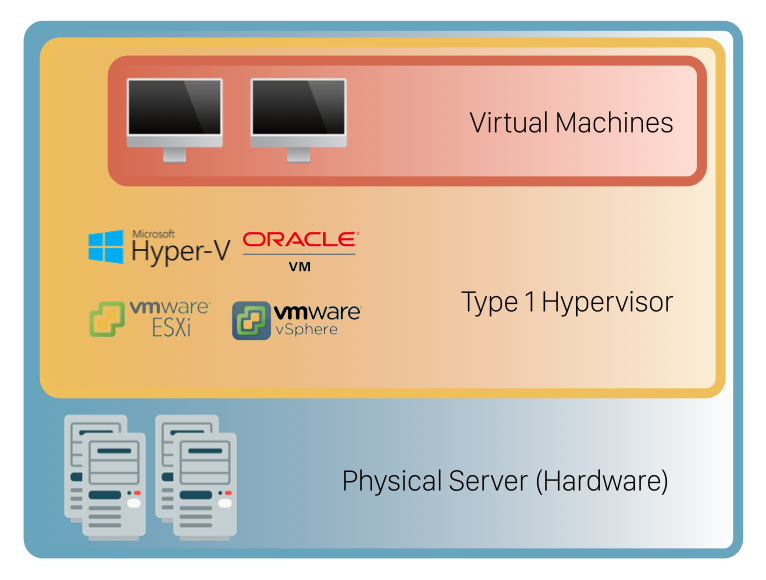
Examples of Type 1 Hypervisors:
- VMware ESXi: A leading hypervisor used in enterprise environments, known for its robustness and extensive feature set.
- Microsoft Hyper-V: Integrated into Windows Server, Hyper-V is a popular choice for organizations that already rely on Microsoft infrastructure.
- Xen: An open-source hypervisor that powers many large-scale cloud environments, including Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine): A Linux-based hypervisor that is part of the Linux kernel, KVM is known for its flexibility and integration with the Linux ecosystem.
Usefulness and Benefits of Type 1 Hypervisors:
- Performance: Since Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the hardware, they offer near-native performance, making them ideal for demanding workloads.
- Scalability: These hypervisors can efficiently manage large numbers of VMs, making them suitable for data centers and cloud providers.
- Security: With direct access to hardware, Type 1 hypervisors can offer robust security features, including isolation between VMs and protection from vulnerabilities that might affect the host operating system.
- Resource Efficiency: By eliminating the overhead of a host operating system, Type 1 hypervisors make better use of physical resources, resulting in lower latency and higher throughput.
Type 2 Hypervisors (Hosted)
Type 2 hypervisors, also known as hosted hypervisors, run on top of a host operating system, like any other software application. They are generally easier to set up and use, making them suitable for smaller-scale deployments, testing, and development environments.
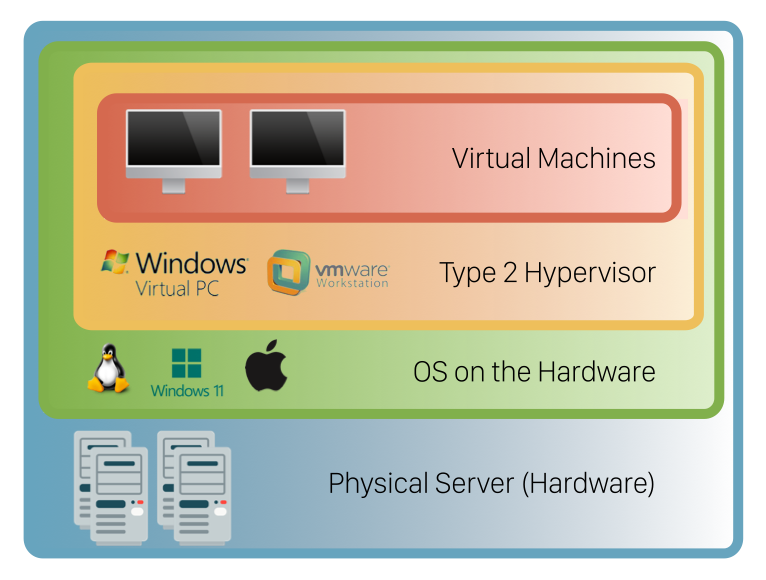
Examples of Type 2 Hypervisors:
- VMware Workstation/Fusion: These are desktop virtualization products from VMware that allow users to run multiple operating systems on their PCs or Macs.
- Oracle VM VirtualBox: A free and open-source hypervisor that supports a wide range of guest operating systems and is popular for personal use and small-scale virtualization.
- Parallels Desktop: A hypervisor designed for Mac users, allowing them to run Windows alongside macOS.
Usefulness and Benefits of Type 2 Hypervisors:
- Ease of Use: Type 2 hypervisors are typically more user-friendly and easier to install, making them accessible to users with less technical expertise.
- Cost-Effective: These hypervisors are often free or low-cost, making them ideal for individuals, small businesses, and educational institutions.
- Flexibility: With the ability to run multiple operating systems on a single machine, Type 2 hypervisors are perfect for testing, development, and training purposes.
- Compatibility: Because they run on top of an existing OS, Type 2 hypervisors can take advantage of the host system’s drivers and hardware support, making them compatible with a wide range of devices.
Usefulness of Hypervisors in Various Environments
Hypervisors play a pivotal role in various computing environments, each with its specific requirements and constraints.
Data Centers and Cloud Providers:
- Resource Optimization: Hypervisors enable the efficient use of server resources by running multiple VMs on a single physical machine, reducing hardware costs.
- Scalability: They allow data centers to scale operations quickly by adding or removing VMs without the need for additional hardware.
- Flexibility: Cloud providers can offer diverse services to customers by leveraging hypervisors to run different types of workloads on the same infrastructure.
Development and Testing:
- Environment Isolation: Developers can create isolated environments for testing different operating systems, applications, and configurations without affecting their main system.
- Rapid Provisioning: Hypervisors allow developers to quickly spin up and tear down VMs, speeding up the development and testing cycles.
Disaster Recovery:
- VM Snapshots: Hypervisors provide the ability to take snapshots of VMs, making it easier to restore systems to a previous state in case of failure.
- Replication: Virtual machines can be replicated and moved between hosts, facilitating robust disaster recovery plans.
Desktop Virtualization:
- BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): Hypervisors enable employees to run corporate environments on personal devices, enhancing flexibility while maintaining security.
- Centralized Management: IT departments can centrally manage desktop environments, reducing the complexity of supporting diverse user hardware.
Benefits of Using Hypervisors
Hypervisors offer several key benefits that make them a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure:
Cost Efficiency:
- By consolidating multiple workloads onto fewer physical servers, organizations can significantly reduce hardware, power, and cooling costs.
Improved Resource Utilization:
- Hypervisors allow for better utilization of physical resources, ensuring that CPU, memory, and storage are not wasted.
Enhanced Security:
- Hypervisors provide isolation between VMs, reducing the risk that a compromise in one VM will affect others.
High Availability and Redundancy:
- Features like VM migration and load balancing ensure that applications remain available, even if one physical server fails.
Simplified Management:
- Centralized management tools for hypervisors make it easier to monitor, control, and maintain large numbers of VMs across different physical hosts.
Hypervisors have become an integral part of the IT landscape, enabling the virtualization that powers cloud computing, enterprise data centers, and even everyday desktop computing. Whether you choose a Type 1 or Type 2 hypervisor depends on your specific needs, but both types offer substantial benefits, from cost savings to enhanced flexibility and security. As organizations continue to adopt virtualization technologies, the role of hypervisors will only grow in importance, making them a crucial component of any modern IT strategy.








