
Understanding SIM Swap Fraud and How To Prevent It
In the digital age, the seamless operation of our mobile devices is critical. One often overlooked aspect of mobile security is the vulnerability associated with SIM swapping, a sophisticated form of identity theft that can lead to severe financial and personal consequences. This blog delves into what SIM swapping is, how it works, and some notable case examples that highlight its devastating effects, including significant cases from Africa.
What is SIM Swapping?
SIM swapping, also known as SIM hijacking, is a technique used by fraudsters to take control of a victim’s phone number. This allows them to intercept calls and text messages, including those that are part of two-factor authentication (2FA) processes used by banks, email services, and other platforms. By doing so, attackers can gain access to sensitive personal information and accounts.
How SIM Swapping Works
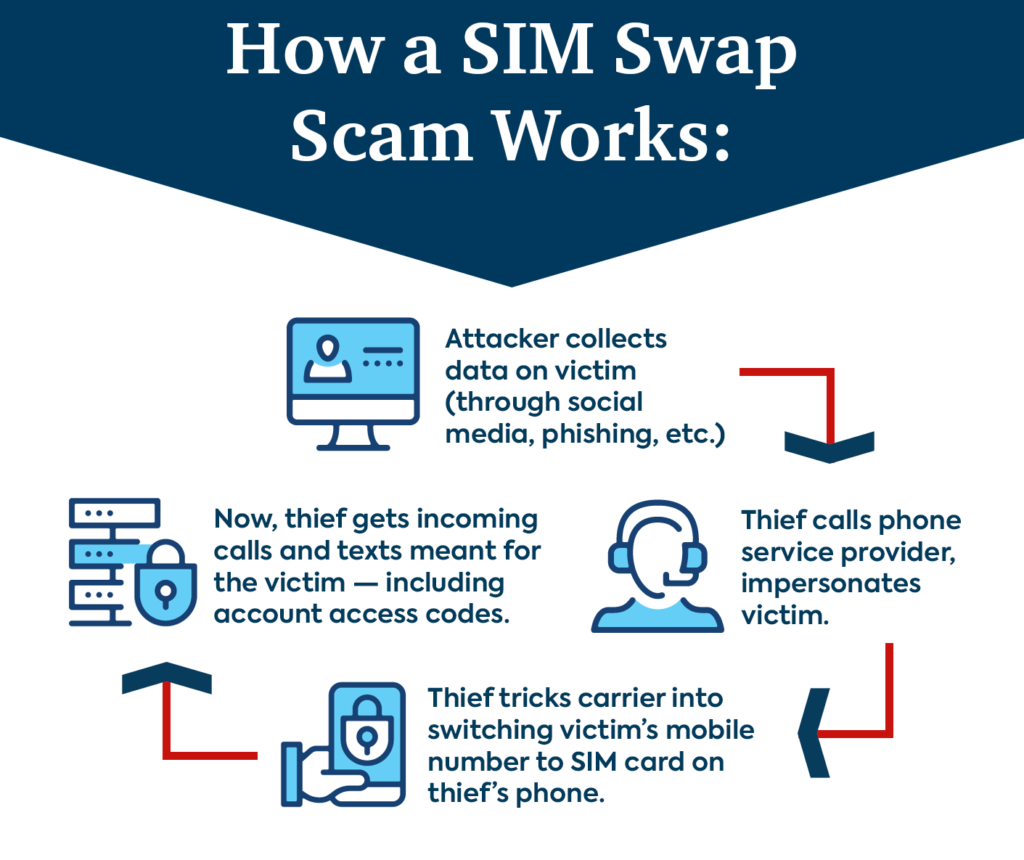
- Gathering Personal Information: Attackers often begin by gathering personal information about their target through phishing emails, social engineering, or purchasing data from the dark web.
- Contacting the Mobile Carrier: The attacker contacts the victim’s mobile carrier, impersonating the victim. They use the gathered personal information to convince the carrier to transfer the victim’s phone number to a new SIM card controlled by the attacker.
- Executing the Swap: Once the carrier approves the transfer, the victim’s phone loses service, and the attacker now receives all calls and messages intended for the victim.
- Gaining Access to Accounts: With control over the victim’s phone number, the attacker can reset passwords for various online accounts, using 2FA codes sent via SMS. This enables them to access email, bank accounts, social media, and more.
Notable SIM Swapping Cases
1. Michael Terpin’s Case
In 2017, cryptocurrency investor Michael Terpin fell victim to a SIM swapping attack, resulting in the loss of nearly $24 million in digital currencies. Terpin sued his mobile carrier, AT&T, alleging that the company’s negligence allowed the attacker to gain control of his phone number. The case highlighted the significant risks and financial impacts associated with SIM swapping, as well as the potential legal liabilities for mobile carriers.
2. Jack Dorsey’s Twitter Hack
In August 2019, Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey experienced a high-profile SIM swapping attack. Hackers gained control of Dorsey’s phone number and used it to post offensive messages on his Twitter account. Although the attack was quickly mitigated, it underscored the vulnerability of even high-profile individuals to SIM swapping and the potential for reputational damage.
3. The OCG Case in the UK
In 2020, the UK’s National Crime Agency (NCA) dismantled an organized crime group (OCG) responsible for a series of SIM swapping attacks targeting celebrities and sports stars. The group managed to steal personal data, cryptocurrency, and money by taking over the victims’ phone numbers. The case demonstrated the sophisticated and coordinated nature of SIM swapping operations and the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
Also Check
4. Ghana: The Mobile Money Scam
In Ghana, SIM swapping is a growing concern due to the widespread use of mobile money services. In 2019, the Cyber Crime Unit of the Ghana Police Service reported several cases where fraudsters used SIM swapping to steal significant amounts of money from mobile money accounts. One notable case involved a syndicate that managed to swap the SIM cards of over 50 individuals, accessing their mobile money accounts and transferring funds to various accounts under the control of the fraudsters. The case prompted mobile operators and financial institutions in Ghana to enhance their security protocols.
5. Nigeria: The Case of the Bank Employee
In Nigeria, SIM swapping has become a prevalent method of bank fraud. In a high-profile case in 2020, a bank employee was arrested for collaborating with fraudsters to carry out SIM swap fraud. The employee provided personal details of bank customers to the fraudsters, who then used the information to swap SIM cards and gain access to the victims’ bank accounts. The fraudsters were able to siphon off millions of Naira before the scheme was uncovered. This case highlighted the insider threat and the need for stringent security measures within financial institutions.
Protecting Yourself Against SIM Swapping
1. Strengthen Account Security
- Use Authenticator Apps: Instead of relying on SMS-based 2FA, use authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy.
- Secure Your Email: Your email is often the gateway to your other accounts. Use strong, unique passwords and enable 2FA for your email accounts.
2. Increase Mobile Carrier Security
- Add a PIN to Your Account: Contact your mobile carrier to set up a PIN or password that must be provided before any changes can be made to your account.
- Inform Carrier of Threats: Notify your carrier if you believe you are at risk of a SIM swap attack so they can take additional precautions.
3. Monitor Your Accounts
- Regularly Check for Unauthorized Activity: Keep an eye on your bank accounts, email, and other sensitive accounts for any signs of suspicious activity.
- Be Wary of Phishing Attempts: Avoid clicking on links or providing personal information in response to unsolicited emails or messages.
Conclusion
SIM swapping is a potent and increasingly common threat in today’s interconnected world, with significant incidents reported globally, including in Africa. By understanding how it works and taking proactive steps to protect your personal information and accounts, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to this type of fraud. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your digital security to safeguard against SIM swapping attacks.








